A vehicle’s suspension system is responsible for absorbing the shock and impact of the road, providing a smooth ride, and ensuring the tires remain in contact with the road surface. Two critical components of the suspension system are shocks and struts, which work together to improve handling, increase safety, and enhance driving comfort. While shocks and struts may appear similar, they serve different functions and have some key differences.
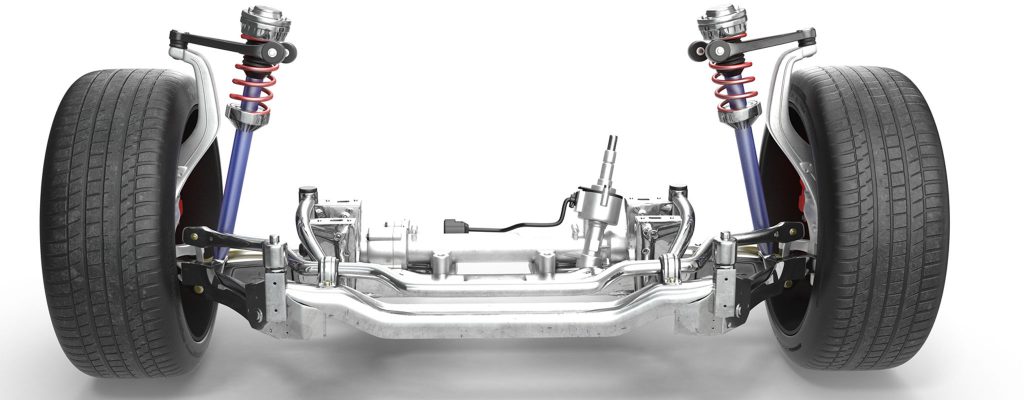
What are shocks?
Shocks, also called shock absorbers, are cylindrical devices that control the movement of the vehicle’s suspension system. They use hydraulic or gas pressure to dampen the movement of the springs and suspension, reducing the bouncing and vibrations caused by road irregularities. Shocks are typically mounted vertically and placed between the vehicle’s frame and its wheels. They help keep the wheels in contact with the road surface, providing better traction, stability, and control. Shocks are commonly used in most vehicles, including cars, trucks, and SUVs.
What are struts?
Struts are a more complex component than shocks, as they serve both a structural and functional role in the suspension system. Struts are mounted horizontally and are an integral part of the suspension assembly, combining the shock absorber with other suspension components such as springs and control arms. The strut assembly helps to support the weight of the vehicle, maintain the ride height, and provide additional stiffness to the suspension system. Struts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles and some rear-wheel-drive vehicles.
Differences between shocks and struts:
While both shocks and struts serve to dampen the movement of the suspension system, there are some key differences between the two components. One significant difference is their position and orientation. Shocks are mounted vertically, while struts are mounted horizontally. Additionally, struts are an integral part of the suspension assembly and serve a structural role, while shocks are separate components that function solely to absorb shocks and vibrations.
Another difference between shocks and struts is the type of suspension system they are commonly used in. Shocks are typically used in vehicles with independent suspension, while struts are more commonly found in vehicles with a MacPherson strut suspension. Independent suspension uses separate components for each wheel, while MacPherson strut suspension combines several suspension components into a single unit.
Benefits of shocks and struts:
The benefits of shocks and struts include improved handling, increased safety, and enhanced driving comfort. Shocks and struts work together to keep the wheels in contact with the road surface, providing better traction, stability, and control. They also reduce the wear and tear on other suspension components, such as tires, brakes, and steering components, extending their lifespan and reducing maintenance costs.
Shocks and struts also improve safety by reducing the likelihood of accidents caused by loss of control, such as skidding or sliding. By maintaining a smooth ride, they also enhance driving comfort, reducing driver fatigue and stress.
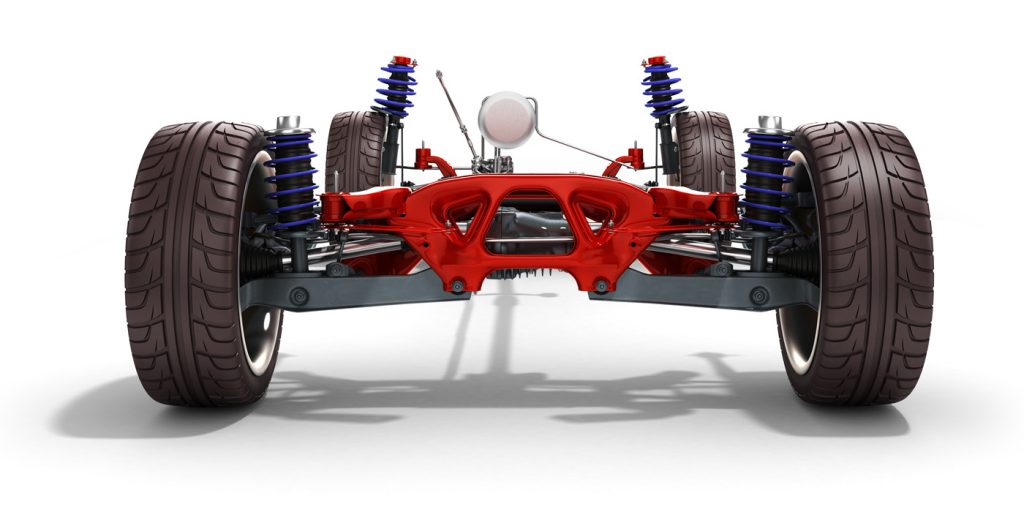

Conclusion:
In summary, shocks and struts are critical components of a vehicle’s suspension system that work together to improve handling, increase safety, and enhance driving comfort. While both components serve to dampen the movement of the suspension system, they have some key differences, including their position and orientation, the type of suspension system they are commonly used in, and their role in the suspension assembly. Whether your vehicle uses shocks or struts, it’s important to maintain them regularly to ensure optimal performance and safety.
For the largest selection of shocks and struts in Canada, visit AutoPartsWAY.ca